DNA Fingerprinting (RFLP and VNTRs)
a)
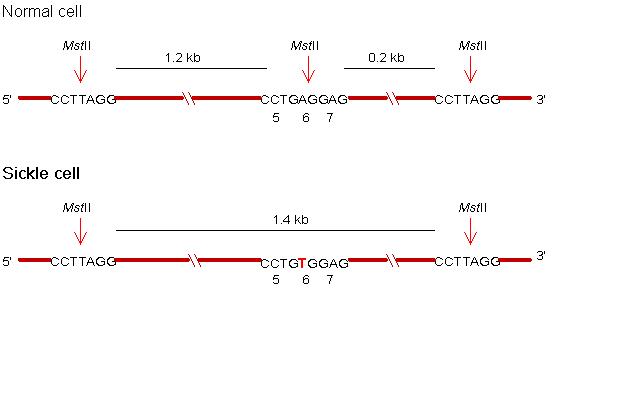
The most well known example is the RFLP due to globin
gene mutation.
In the normal cell, the sequence corresponding to 5th to 7th amino acids of the globin peptide is CCTGAGGAG, which can be recognized by the restriction enzyme MstII. In the sickle cell, one base is mutated from A to T, making the site unrecognizable by MstII. Thus, MstII will generate 0.2 kb and 1.2 kb fragments in the normal cell, but generate 1.4 kb fragment in the sickle cell. These different fragments can be detected by southern blotting.
Variable Number of Tandem Repeat (VNTR) Polymorphism
Variable Number of Tandem Repeat (VNTR) Polymorphism may result from unequal crossover. It is due to significant sequence homology, the repetitive sequence region of a chromatid may not line up exactly with its corresponding region in a homogenous chromatid or identical sister chromatid. As a result, different number of repeat units may be generated during meiosis.
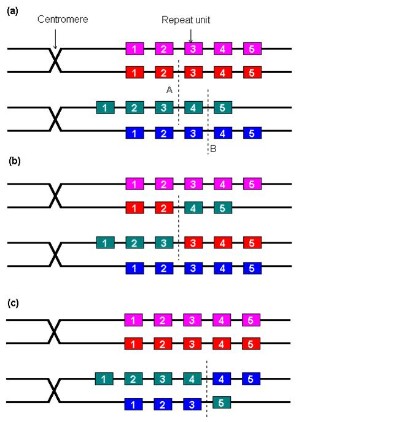
(a) Two pairs of sister chromatids line up during meiosis. A
repetitive region of one chromatid (the third one) does not line up exactly
with its corresponding region in other chromatids.
(b) Strand breaks on nonsister
chromatids (along line A) will result in unequal crossover, producing different
number of repeat units in these chromatids.
(c) Strand breaks on sister chromatids (along line B) also produce different repeats. In this case, it is called sister chromatid exchange. The detailed mechanism of DNA crossover in (b) and (c) may be explained by the Holliday model.
Other applications of Southern Blot Techniques
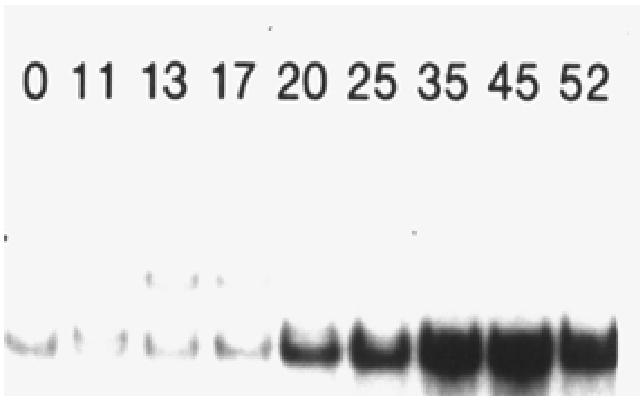
Gene Expression
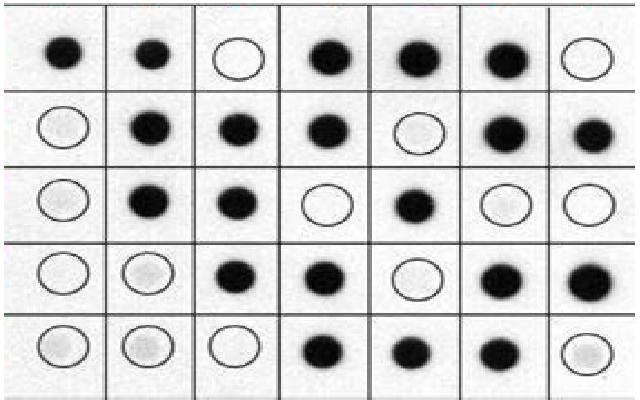
Dot or slot blot
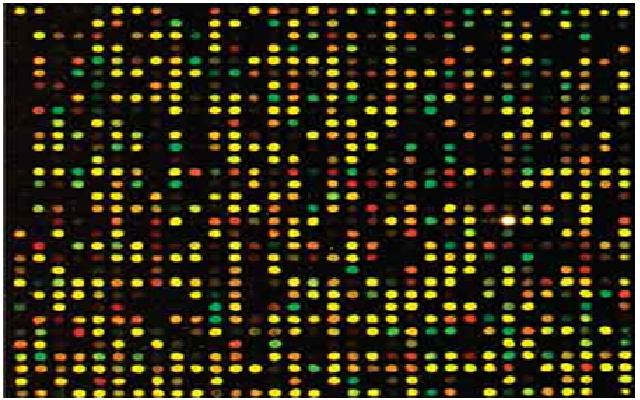
Microarray analysis